The ads that are showing will be removed once we have the demanded number of downloads.
Follow our FB Page : https://www.facebook.com/ITnetworkyy
A Switch is a networking device that connects devices together in a network by using packet switching to receive, process and forward data to the destination device.
A network switch is a multiple network switch that uses hardware addresses to process and forward data at LINK LAYER which is the Layer 2 of the OSI model.
A switch also can be in Layer 2 and Layer 3!
In the case of a layer 3 Switch or we call it a multilayer switch which can also make routing in the Layer 3 (Network Layer) of the OSI Model.
Layer 2 Switches make Switching based on the MAC Table, in fact they conserve a mac address table and forward the packets using the MAC ADDRESS Table.
This will provide us an efficient use of bandwidth.
Switches can provide equally power over ethernet or PoE, also a switch can participate in security which is a deeper topic.
What is a Broadcast domain?
A broadcast domain is a logical division of a network in which all nodes can reach each other by broadcast at DATA LINK Layer (Layer 2 of the OSI Model).
A broadcast dmain can be within the same local area network segment or it can be bridged to other local area network segments.
Any computer connected to the same switch is a member of the same broadcast domain.
Separating the network with VLANs creates new broadcast domain equally.
One VLAN equals 1 Broadcast domain.
Routers which are components of the Layer 3 (Network Layer) of the OSI Layer form Boundries.
What is a MAC address?
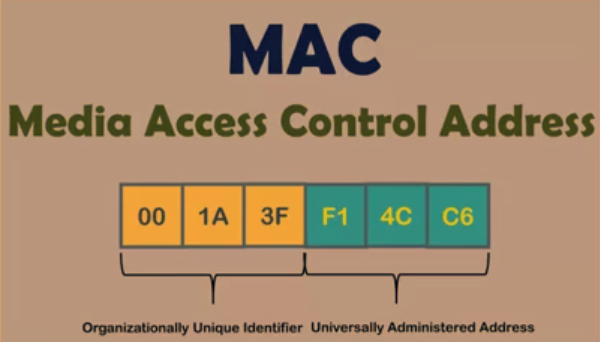
A MAC Address = Media Access Control Address is a 6 byte unique identifier assigned to network interfaces for communications at data link Layer (Layer 2 OSI layer).
Mac addresses are used as network address for most IEEE technologies including Ethernet and WiFi.
Logically MAC Addresses are used in the MEDIA ACCESS CONTROL protocol, sublayer of the OSI Model.
6 bytes = OUI (Organizationally Unique Identifier) + UAA (Universally Administered Address)
OUI (Organizationally Unique Identifier) is a 24 bit number that uniquely identifies a vendor, manufacturer or other organizations.
In the capture you can see the first part containing the OUI.
The second portion of a MAC Address is UAA or Universally Administreded Address.
The UAA is a uniquely assigned to a device by its manufacturer. (Just remember this, don't complicate things).
What is an Ethernet Frame :
An Ethernet packet (or Frame) has :
1- Preamble ( Provides SYNCHRONIZATION; means checks whether a packet is coming. )
2- SFD (Start of Frame Delimiter : Responsible for specifying the beginning of destination MAC ADDRESS on an ethernet packet.)
3- Receiver MAC ADDRESS (Or the destination MAC)
4- Sender MAC ADDRESS (Or the source MAC)
5- An Optional VLAN TAG
6- A Type field
7- A payload
and
8- The CRC Checksum
Basic Switching Process
If the destination MAC addess is found in the CAM table of the switch, the switch sends the frame out of the corresponding port : This process is called FORWARDING.
If the destination MAC address can not be found in the CAM Table, then the frame is sent to all other ports in the same VLAN and this process is called : FLOODING.
If the destination MAC address of the receiving frame is a BROADCAST ADDRESS which is :
FFFF:FFFF:FFFF; this time the frame is sent to all the ports in the same VLAN and this process is called also FLOODING.
VLANs
VLAN = Virtual Local Area Network
1 VLAn = 1 Broadcast Domain
We use VLANs for isolation, this way different VLANs can not communicate with each other without a L3 device (A L3 Device could be a router or a L3 Switch).
Benefits of Using VLANs
- Easy management
- Easy Error detection
- Better performance
-Cost reduction (less routers which are more expensive)
-Security
Remember this :
- There are two modes in switch ports : ACCESS or TRUNK
- ACCESS = 1 VLAN = Access is known also as UNTAGGED
- TRUNK = Multiple VLANs = is known also as TAGGED.
LAYER 3 SWITCHING
A Layer 3 Switch has SVI interfaces that could support routing.
Examples of Multilayer switches
- Cisco 4500
- Cisco 6500
These models of multilayer switches can make Layer 2 switching and Layer 3 Routing in the same time and in this case we'll no longer need routers.
In order to activate the routing capabilities on a Layer 3 switch we need to put this command in the previliged mode
#ip routing (if you do not put this command than your switch will never build a router table)
Than we will need to assign IP addresses to SVI interfaces.






Comments
Download Free Demo: https://www.passitcertify.com/cisco/350-401-questions.html
No 정읍 출장마사지 deposit free spins no deposit casino 여수 출장마사지 slots – 양주 출장마사지 No deposit free spins no 경산 출장마사지 deposit bonus casino slots – No deposit free spins no deposit 계룡 출장안마 bonus casinos – No deposit free spins no deposit bonus casinos – No